Abstract
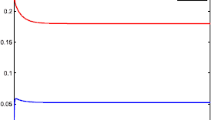
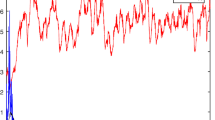
This paper proposes two new stochastic non-autonomous SEIS epidemic dynamical models with latent and active patients. For the non-autonomous periodic system, we first obtain the sufficient conditions for the existence of nontrivial positive periodic solution by constructing some suitable stochastic Lyapunov functions with regime switching. Then we prove the existence of ergodic stationary distribution of the stochastic SEIS epidemic model with Markov conversion by using the stochastic qualitative theory. At last, some rigorous computer numerical simulations illustrate our theoretical results. The results show that the large random disturbance can destroy the periodic solution and the ergodic stationary distribution.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kermack, W.O., McKendrick, A.G.: A contributions to the mathematical theory of epidemics (part I). Proc. R. Soc. A 115, 700–721 (1927)
Zhao, Y.N., Jiang, D.Q.: The threshold of a stochastic SIS epidemic model with vaccination. Appl. Math. Comput. 243, 718–727 (2014)
Meng, X.Z., Zhao, S.N., Feng, T., Zhang, T.H.: Dynamics of a novel nonlinear stochastic SIS epidemic model with double epidemic hypothesis. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 433, 227–242 (2016)
Miao, A.Q., Wang, X.Y., Zhang, T.Q., Wang, W., Sampath Aruna Pradeep, B.G.: Dynamical analysis of a stochastic SIS epidemic model with nonlinear incidence rate and double epidemic hypothesis. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2017(1), 226 (2017)
Qi, H.K., Liu, L.D., Meng, X.Z.: Dynamics of a non-autonomous stochastic SIS epidemic model with double epidemic hypothesis. Complexity 2017, 14 (2017)
Gray, A., Greenhalgh, D., Hu, L., Mao, X.R., Pan, J.: A stochastic differential equation SIS epidemic model. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 71(3), 876–902 (2011)
McCluskey, C.C.: Complete global stability for an SIR epidemic model with delay—distributed or discrete. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 11(1), 55–59 (2010)
d’Onofrio, A.: On pulse vaccination strategy in the SIR epidemic model with vertical transmission. Appl. Math. Lett. 18(7), 729–732 (2005)
Miao, A.Q., Zhang, J., Zhang, T.Q., Sampath Aruna Pradeep, B.G.: Threshold dynamics of a stochastic SIR model with vertical transmission and vaccination. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2017, 10 (2017)
Yang, Q.S., Jiang, D.Q., Shi, N.Z., Ji, C.Y.: The ergodicity and extinction of stochastically perturbed SIR and SEIR epidemic models with saturated incidence. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 388(1), 248–271 (2012)
Lahrouza, A., Omaria, L., Kiouachb, D., Belmaatic, A.: Complete global stability for an SIRS epidemic model with generalized non-linear incidence and vaccination. Appl. Math. Comput. 218(11), 6519–6525 (2012)
Zhao, J.D., Wang, L.S., Han, Z.X.: Stability analysis of two new SIRS models with two viruses. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2017, 1–10 (2017)
Li, C.H., Tsai, C.C., Yang, S.Y.: Analysis of epidemic spreading of an SIRS model in complex heterogeneous networks. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 19(4), 1042–1054 (2014)
Gao, S.J., Chen, L.S., Nieto, J.J., Torres, A.: Analysis of a delayed epidemic model with pulse vaccination and saturation incidence. Vaccine 24, 6037–6045 (2006)
Meng, X.Z., Wu, Z.T., Zhang, T.Q.: The dynamics and therapeutic strategies of a SEIS epidemic model. Int. J. Biomath. 6(5), 1350029 (2013)
Li, F., Meng, X.Z., Wang, X.Z.: Analysis and numerical simulations of a stochastic SEIQR epidemic system with quarantine-adjusted incidence and imperfect vaccination. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2018, 7873902 (2018)
Zhang, Y., Chen, S.H., Gao, S.J., Wei, X.: Stochastic periodic solution for a perturbed non-autonomous predator–prey model with generalized nonlinear harvesting and impulses. Physica A 486, 347–366 (2017)
Leng, X.N., Feng, T., Meng, X.Z.: Stochastic inequalities and applications to dynamics analysis of a novel SIVS epidemic model with jumps. J. Inequal. Appl. 2017(1), 138 (2017)
Zhou, Y.L., Yuan, S.L., Zhao, D.L.: Threshold behavior of a stochastic SIS model with Levy jumps. Appl. Math. Comput. 275, 255–267 (2016)
Liu, L.D., Meng, X.Z.: Optimal harvesting control and dynamics of two-species stochastic model with delays. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2017(1), 18 (2017)
Liu, M., Fan, M.: Permanence of stochastic Lotka–Volterra systems. J. Nonlinear Sci. 27, 425–452 (2017)
Lv, X.J., Wang, L., Meng, X.Z.: Global analysis of a new nonlinear stochastic differential competition system with impulsive effect. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2017, 296 (2017)
Liu, M.: Optimal harvesting policy of a stochastic predator-prey model with time delay. Appl. Math. Lett. 48, 102–108 (2015)
Ma, H.J., Jia, Y.M.: Stability analysis for stochastic differential equations with infinite Markovian switchings. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 435, 593–605 (2016)
Wang, Y.H., Pan, Z.T., Li, Y., Zhang, W.H.: H\(_{\infty }\) control for nonlinear stochastic Markov systems with time-delay and multiplicative noise. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 30, 1–23 (2017)
Zhang, Y., Fan, K.G., Gao, S.J., Chen, S.H.: A remark on stationary distribution of a stochastic SIR epidemic model with double saturated rates. Appl. Math. Lett. 76, 46–52 (2018)
Liu, X.K., Li, Y., Zhang, W.H.: Stochastic linear quadratic optimal control with constraint for discrete-time systems. Appl. Math. Comput. 228, 264–270 (2014)
Zhao, Y., Yuan, S., Zhang, T.: The stationary distribution and ergodicity of a stochastic phytoplankton allelopathy model under regime switching. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 37, 131–142 (2016)
Meng, X.Z., Wang, L., Zhang, T.H.: Global dynamics analysis of a nonlinear impulsive stochastic chemostat system in a polluted environment. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 6(3), 865–875 (2016)
Wang, Y., Jiang, D.Q., Hayat, T., Ahmad, B.: A stochastic HIV infection model with T-cell proliferation and CTL immune response. Appl. Math. Comput. 315, 477–493 (2017)
Tan, C., Zhang, W.H.: On observability and detectability of continuous-time stochastic Markov jump systems. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 28(4), 830–847 (2015)
Bai, Z., Zhou, Y.: Existence of two periodic solutions for a non-autonomous SIR epidemic model. Appl. Math. Model. 35(1), 382–391 (2011)
Kuniya, T.: Existence of a nontrivial periodic solution in an age-structured SIR epidemic model with time periodic coefficients. Appl. Math. Lett. 27, 15–20 (2014)
Zhang, S.Q., Meng, X.Z., Feng, T., Zhang, T.H.: Dynamics analysis and numerical simulations of a stochastic non-autonomous predator–prey system with impulsive effects. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 26, 19–37 (2017)
Liu, Q., Jiang, D.Q., Hayat, T., Ahmad, B.: Periodic solution and stationary distribution of stochastic SIR epidemic models with higher order perturbation. Physica A 482, 209–217 (2017)
Liu, Q., Jiang, D.Q.: Periodic solution and stationary distribution of stochastic predator–prey models with higher-order perturbation. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2017, 1–20 (2017)
Li, Z.X., Chen, L.S., Liu, Z.J.: Periodic solution of a chemostat model with variable yield and impulsive state feedback control. Appl. Math. Model. 36(3), 1255–1266 (2012)
Luo, Q., Mao, X.R.: Stochastic population dynamics under regime switching. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 334(1), 69–84 (2007)
Settati, A., Lahrouz, A.: Stationary distribution of stochastic population systems under regime switching. Appl. Math. Comput. 244, 235–243 (2014)
Mao, X.R.: Stochastic Differential Equations and Their Applications. Horwood, Chichester (1997)
Khasminskii, R.: Stochastic Stability of Differential Equations. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Mao, X.R., Marion, G., Renshaw, E.: Environmental brownian noise suppresses explosions in population dynamics. Stoch. Proc. Appl. 97, 95–110 (2002)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the SDUST Research Fund (2014TDJH102), and the Research Fund for the Taishan Scholar Project of Shandong Province of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, H., Leng, X., Meng, X. et al. Periodic Solution and Ergodic Stationary Distribution of SEIS Dynamical Systems with Active and Latent Patients. Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst. 18, 347–369 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12346-018-0289-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12346-018-0289-9
Keywords
- Stochastic SEIS dynamical model
- Periodic solution
- Ergodic stationary distribution
- Computer numerical simulations
- Lyapunov function