Abstract
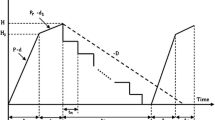
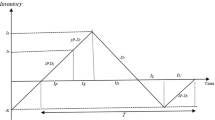
This paper deals with an economic production quantity (EPQ) inventory model with reworkable defective items when a given multi-shipment policy is used. In this work, it is assumed that in each cycle, the rework process of all defective items starts when the regular production process finishes. After the rework process, a portion of reworked items fails. This portion becomes scrap and only the perfect finished items can be delivered to customers at the end of rework process. A profit function is derived to model the inventory problem and it is shown that the profit function is concave. Due to the complexity of the optimization problem, an algorithm is developed to determine the optimal values of manufacturing lot size and price such that the long-run average profit function is maximized. Furthermore, two special cases are identified and explained. Finally, a numerical example is given to illustrate the applicability of the proposed inventory model.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cárdenas-Barrón LE, Sarkar B, Treviño-Garza G (2013) An improved solution to the replenishment policy for the EMQ model with rework and multiple shipments. Appl Math Model 37(7):5549–5554
Cárdenas-Barrón LE (2009a) Economic production quantity with rework process at a single-stage manufacturing system with planned backorders. Comput Ind Eng 57(3):1105–1113
Cárdenas-Barrón LE (2009b) On optimal batch sizing in a multi-stage production system with rework consideration. Eur J Oper Res 196(3):1238–1244
Cárdenas-Barrón LE (2008) Optimal manufacturing batch size with rework in a single-stage production system—a simple derivation. Comput Ind Eng 55(4):758–765
Cárdenas-Barrón LE (2007) On optimal manufacturing batch size with rework process at single-stage production system. Comput Ind Eng 53(1):196–198
Chiu SW, Lee CH, Chiu YSP, Cheng FT (2013) Intra-supply chain system with multiple sales locations and quality assurance. Expert Syst Appl 40(7):2669–2676
Chiu SW, Chen KK, Chiu YSP, Ting CK (2012a) Note on the mathematical modeling approach used to determine the replenishment policy for the EMQ model with rework and multiple shipments. Appl Math Lett 25(11):1964–1968
Chiu SW, Chiu YSP, Yang JC (2012b) Combining an alternative multi-delivery policy into economic production lot size problem with partial rework. Expert Syst Appl 39(3):2578–2583
Chiu S, Lin H, Wu M, Yang J (2011a) Determining replenishment lot size and shipment policy for an extended EPQ model with delivery and quality assurance issues. Sci Iran Trans E Ind Eng 18(6):1537–1544
Chiu YSP, Liu SC, Chiu CL, Chang HH (2011b) Mathematical modeling for determining the replenishment policy for EMQ model with rework and multiple shipments. Math Comput Model 54(9–10):2165–2174
Chen K-K, Wu M-F, Chiu SW, Lee C-H (2012) Alternative approach for solving replenishment lot size problem with discontinuous issuing policy and rework. Expert Syst Appl 39(2):2232–2235
Chen CH, Khoo MBC (2009) Optimum process mean and manufacturing quantity settings for serial production system under the quality loss and rectifying inspection plan. Comput Ind Eng 57(3):1080–1088
Chen JM, Chen LT (2007) Periodic pricing and replenishment policy for continuously decaying inventory with multivariate demand. Appl Math Model 31(9):1819–1828
Chung KJ (2011) The economic production quantity with rework process in supply chain management. Comput Math Appl 62(6):2547–2550
Hong K, Lee C (2013) Optimal time-based consolidation policy with price sensitive demand. Int J Prod Econ 143(2):275–284
Jamal AMM, Sarker BR, Mondal S (2004) Optimal manufacturing batch size with rework process at a single-stage production system. Comput Ind Eng 47(1):77–89
Karakul M, Chan LMA (2010) Joint pricing and procurement of substitutable products with random demands—a technical note. Eur J Oper Res 201(1):324–328
Khan LR, Sarker RA (2002) An optimal batch size for a JIT manufacturing system. Comput Ind Eng 42(2–4):127–136
Krishnamoorthi C, Panayappan S (2012) An EPQ model with imperfect production systems with rework of regular production and sales return. Am J Oper Res 2(2):225–234
Lin H-D, Pai F-Y, Chiu SW (2013) A note on “intra-supply chain system with multiple sales locations and quality assurance”. Expert Syst Appl 40(11):4730–4732
Nahapetyan AG, Pardalos PM (2008) A bilinear reduction based algorithm for solving capacitated multi-item dynamic pricing problems. Comput Oper Res 35(5):1601–1612
Pal B, Sana SS, Chaudhuri K (2013a) A mathematical model on EPQ for stochastic demand in an imperfect production system. J Manuf Syst 32(1):260–270
Pal B, Sana SS, Chaudhuri K (2013b) A stochastic inventory model with product recovery. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 6(2):120–127
Pal B, Sana SS, Chaudhuri K (2013c) Maximising profits for an EPQ model with unreliable machine and rework of random defective items. Int J Syst Sci 44(3):582–594
Pal B, Sana SS, Chaudhuri K (2012) Three-layer supply chain—a production-inventory model for reworkable items. Appl Math Comput 219(2):530–543
Ritha W, Martin N (2013) Replenishment policy for EMQ model with rework, multiple shipments, switching and packaging. Int J Eng Res Technol 2(1):1–8
Roy MD, Sana SS, Chaudhuri K (2014) An economic production lot size model for defective items with stochastic demand, backlogging and rework. IMA J Manag Math 25(2):159–183
Roy MD, Sana SS, Chaudhuri K (2011) An optimal shipment strategy for imperfect items in a stock-out situation. Math Comput Model 54(9–10):2528–2543
Sarker BR, Jamal AAM, Mondal S (2008) Optimal batch sizing in a multi-stage production system with rework consideration. Eur J Oper Res 184(3):915–929
Shamsi R, Haji A, Shadrokh S, Nourbakhsh F (2009) Economic production quantity in reworkable production systems with inspection errors, scraps and backlogging. J Ind Syst Eng 3(3):170–188
Taleizadeh AA, Jalali-Naini SG, Wee HM, Kuo TC (2013) An imperfect multi-product production system with rework. Sci Iran 20(3):811–823
Taleizadeh AA, Cárdenas-Barrón LE, Biabanic J, Nikousokhand R (2012) Multi products single machine EPQ model with immediate rework process. Int J Ind Eng Comput 3(2):93–102
Tapiero CS (2008) Orders and inventory commodities with price and demand uncertainty in complete markets. Int J Prod Econ 115(1):12–18
Treviño-Garza G, Castillo-Villar KK, Cárdenas-Barrón LE (2015) Joint determination of the lot size and number of shipments for a family of integrated vendor-buyer systems considering defective products. Int J Syst Sci, doi:10.1080/00207721.2014.886750 (In press)
Tsai DM, Wu JC (2009) Economic production quantity concerning learning and the reworking of imperfect items. Yugosl J Oper Res 22(2):313–336
Wang CH (2004) The impact of a free-repair warranty policy on EMQ model for imperfect production systems. Comput Oper Res 31(12):2021–2035
Wee HM, Wang WT, Kuo TH, Cheng YL, Huang YD (2014) An economic production quantity model with non-synchronized screening and rework. Appl Math Comput 233:127–138
Wee HM, Widyadana GA (2013) A production model for deteriorating items with stochastic preventive maintenance time and rework process with FIFO rule. OMEGA 41(6):941–954
Wee HM, Wang WT, Cárdenas-Barrón LE (2013) An alternative analysis and solution procedure for the EPQ model with rework process at a single-stage manufacturing system with planned backorders. Comput Ind Eng 64(2):748–755
Yu JCP, Wee HM, Su GB (2013) Revisiting revenue management for remanufactured products. Int J Syst Sci 44(11):2152–2157
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the three anonymous reviewers for their helpful suggestions which have strongly enhanced this paper. The first author would like to thank the financial support of the University of Tehran for this research under grant number 30015-1-03. The research for the third author was supported by Tecnológico de Monterrey Research Group in Industrial Engineering and Numerical Methods 0822B01006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taleizadeh, A.A., Kalantari, S.S. & Cárdenas-Barrón, L.E. Pricing and lot sizing for an EPQ inventory model with rework and multiple shipments. TOP 24, 143–155 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11750-015-0377-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11750-015-0377-9