Abstract
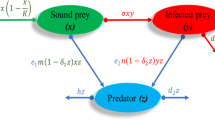
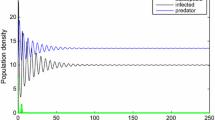
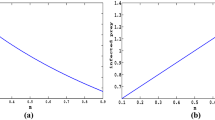
In this paper, we consider an eco-epidemic predator–prey model with Crowley–Martin type functional response and disease in prey population, which is a branch of study in biomathematics which reflects both ecological and epidemiological cases simultaneously. By using Mawhin continuation theorem and constructing a suitable Lyapunov function, we obtained some sufficient conditions for the existence, uniqueness and global attractivity of a positive periodic solution for the predator–prey model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, M.: A diffusive logistic equation with a free boundary and sign-changing coefficient in time-periodic environment. J. Funct. Anal. 270, 483–508 (2016)
Du, Z., Feng, Z., Zhang, X.: Traveling wave phenomena of n-dimensional diffusive predator–prey systems. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 41, 288–312 (2018)
KumarSasma, S., Takeuchi, Y.: Dynamics of a predator-prey system with fear and group defense. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 481, 123471 (2020)
Wang, J., Wei, J., Shi, J.: Global bifurcation analysis and pattern formation in homogeneous diffusive predator–prey systems. J. Differ. Equ. 260, 3495–3523 (2016)
Wang, C., Zhang, X.: Canards, heteroclinic and homoclinic orbits for a slow-fast predator–prey model of generalized Holling type III. J. Differ. Equ. 267, 3397–3441 (2019)
Li, C., Zhu, H.: Canard cycles for predator–prey systems with Holling types of functional response. J. Differ. Equ. 254, 879–910 (2013)
Du, Z., Feng, Z.: Existence and asymptotic behaviors of travelling waves of a modified vector-disease model. Commun. Pure Appl. Anal. 17, 1899–1920 (2018)
Li, S., Wu, J.: Asymptotic behavior and stability of positive solutions to a spatially heterogeneous predator–prey system. J. Differ. Equ. 265, 3754–3791 (2018)
Chen, X., Du, Z.: Existence of positive periodic solutions for a neutral delay predator–prey model with Hassell–Varley type functional response and impulse. Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst. 17, 67–80 (2018)
Upadhyay, R.K., Naji, R.K.: Dynamics of a three species food chain model with Crowley–Martin type function response. Chaos Solitons Fractals 42, 1337–1346 (2009)
Gaines, R., Mawhin, J.: Coincidence Degree and Nonlinear Differential Equations. Springer, Berlin (1977)
Li, X., Lin, X., Liu, J.: Existence and global attractivity of positive periodic solutions for a predator–prey model with Crowley–Martin functional response. Elec. J. Differ. Equ. 2018, 1–17 (2018)
Mortoja, S.G., Panja, P., Mondal, S.K.: Dynamics of a predator–prey model with nonlinear incidence rate, Crowley–Martin type functional response and disease in prey population. Ecol. Genet. Genom. 10, 100035 (2019)
Bairagi, N., Roy, P.K., Chattopadhyay, J.: Role of infection on the stability of a predator–prey system with several response functions—a comparative study. J. Theor. Biol. 248, 10–25 (2007)
Sari, N., Véron, E.A.: Periodic orbits of a seasonal SIS epidemic model with migration. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 423, 1849–1866 (2015)
Zheng, H., Guo, L., Bai, Y., Xia, Y.: Periodic solutions of a non-autonomous predator-prey system with migrating prey and disease infection: via Mawhin coincidence degree theory. J. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 260, 21–37 (2019)
Silva, C.M.: Existence of periodic solutions for periodic eco-epidemic models with disease in the prey. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 453, 383–397 (2017)
Zhu, Y., Wang, K.: Existence and global attractivity of positive periodic solutions for a predator–prey model with modified Leslie–Gower Holling-type II schemes. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 384, 408–408 (2011)
Chen, C., Chen, F.: Conditions for global attractivity of multispecies ecological competition-predator system with Holling-type III functional response. J. Biomath. 19, 136–140 (2004)
Gopalasamy, K.: Stability and Oscillation in Delay Equation of Population Dynamics. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (1992)
Acknowledgements
We express our sincere thanks to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions for improving the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11871251, 11801231 and 11771185).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, M., Yan, S. & Du, Z. Positive Periodic Solutions of an Eco-Epidemic Model with Crowley–Martin type Functional Response and Disease in the Prey. Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst. 19, 56 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12346-020-00392-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12346-020-00392-3
Keywords
- Predator–prey model
- Crowley–Martin functional response
- Global attractivity
- Periodic solution
- Mawhin continuation theorem
- Lyapunov function